- Corporate
- Chemical Products
- Chemical Controller
- Chemical for Paint Booth
- Coil Coating
- Degreasing and Cleaning chemical
- Heat&Cool exchanger (PLATECOIL)
- Hydrophilic
- Manganese Phosphate
- Nano-coating (Pallucid)
- Rolling Oil
- Rust Preventive Product
- Stearate Soap Lubricant/Dry-in-Place Lubricant (PULS)
- Trivalent Chromium/Non-Chromium
- Zinc Phosphate/Iron Phosphate
- Processing Services
- Laboratory Services
- Articles
- What's New
- Contact Us
- Privacy Policy
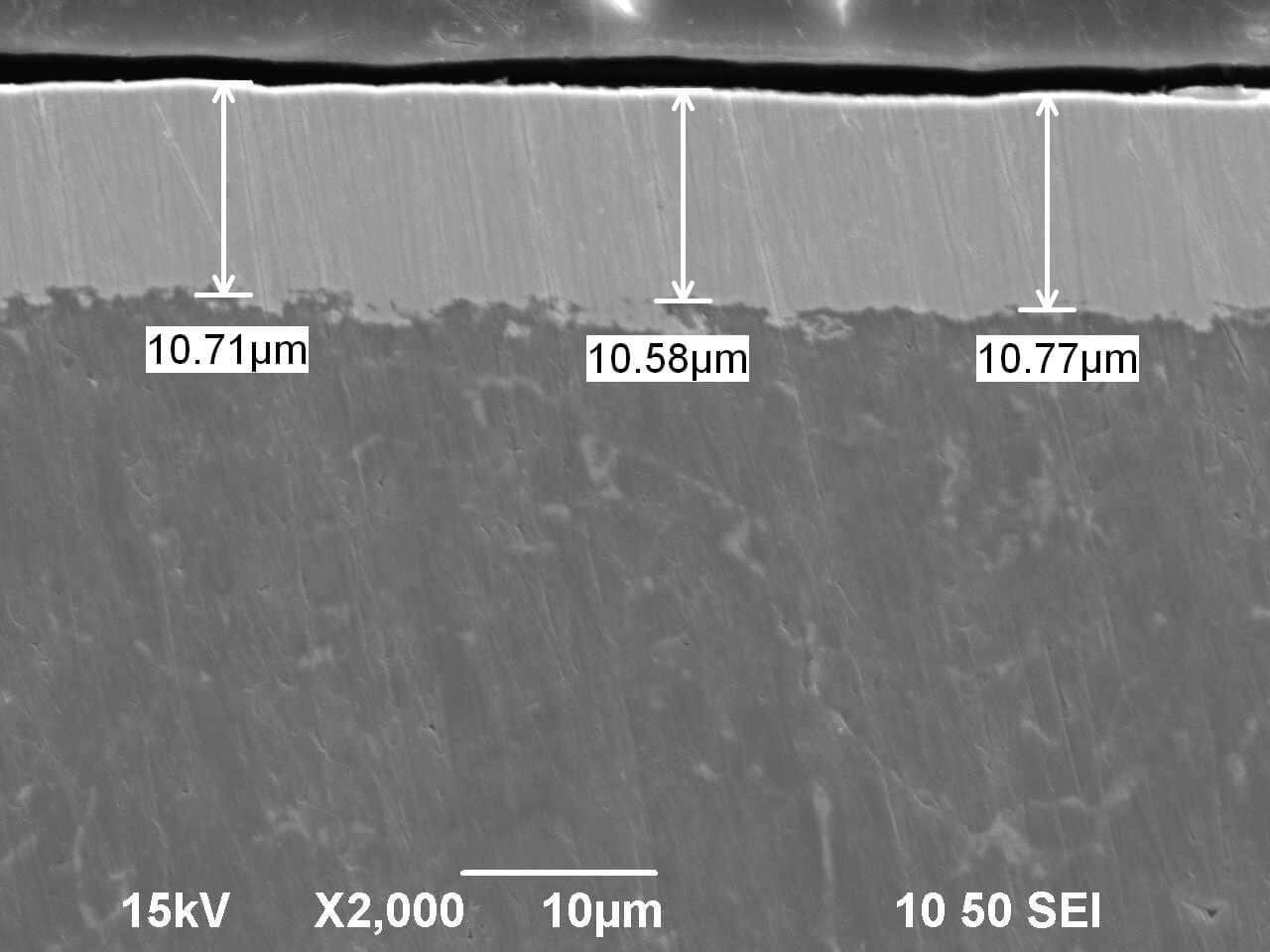 |
Electroless nickel plating (Kanigen®)Kanigen (Electroless Nickel plating: EN plating) generate glossy smooth Nickel plating film to overall parts surface. It is possible to plate on various types of material and various forms of components. It has superior qualities in thickness uniformity, corrosion resistance and abrasion resistance. Electroless plating intends to prolong the life of the material itself and further improve the material’s characteristics. Name “Kanigen” was adopted by combining the first syllable from the words C(K): Catalytic, Ni: Nickel and Gen: Generation Kanigen has been registered as Trademark of Electroless Plating in Japan by Nihon Kanigen (Group Company of Nihon Parkerizing) |
Get the info youâre looking for right now!
If you canât find the answer youâre looking for, weâd love to hear from you â whether youâre curious about features, a sample trial, or even pricingâweâre ready to answer all questions a find the right products for you!
- Smooth coating of surface
- Amorphous(non-porous) plating film
- Available apply to Steel and Aluminium.
- High hardness
- Uniform coating overall surface even for complicated shape
- Available tight range thickness control
- High anticorrosion ability
- Wear resistance
- Against high temporary and high alkaline condition
- Automotive / motorcycle parts
Engine piston, Delivery pipe, Fuel pipe, Turbo-charger
Drive/ Transmission parts
Pinion shaft, EPS shaft, CVT parts, Difference washer, Power steering parts, Clutch cam plate and Hub
Suspension/Brake parts
Break piston, Wheel cylinder, Drum break, Anchor pin, ABS/ASC parts. - Electrical parts/components
Lead frame, Air conditioning part (Scroll, Shoe, Vane), Airbag ECU parts, power control unit PCU.
Product type
Check more of our Product / Process type specifications below.
Frequently Asked Questions
The main difference is that EN does not require an external electric current; instead, it uses an autocatalytic chemical reaction where a reducing agent (like sodium hypophosphite) supplies electrons to the nickel ions (Ni2+). The most significant advantages are:
- Coating Uniformity: EN provides a deposit of uniform thickness across the entire workpiece, even in complex shapes, holes, or recessed areas, which is challenging for electroplating.
- Coating Properties: EN deposits are typically Nickel-Phosphorus (Ni-P), offering excellent Corrosion Resistance and Hardness which can be further enhanced with heat treatment.
The phosphorus content directly influences the properties of the ENP layer. It can be categorized into three main levels which are highly relevant in current applications:
- High-Phos (>10% P): Provides maximum corrosion resistance (in acidic or salt environments) and is non-magnetic.
- Mid-Phos (5-9% P): Offers a balance between hardness and corrosion resistance.
- Low-Phos (1-4% P): Provides the highest hardness and excellent wear resistance. It is often used for high-abrasion applications.
Heat treatment (Baking) is a crucial post-plating step with two main objectives:
- Increase Hardness: Heat causes the amorphous structure of the Nickel-Phosphorus layer to transform into a crystalline structure containing Ni3P precipitates. This significantly increases the hardness and improves wear resistance.
- Improve Adhesion: Heat aids the diffusion of atoms at the interface between the coating and the substrate, thereby enhancing the coating's adhesion to the base material, especially for steel and aluminum.













