- Corporate
- Chemical Products
- Chemical Controller
- Chemical for Paint Booth
- Coil Coating
- Degreasing and Cleaning chemical
- Heat&Cool exchanger (PLATECOIL)
- Hydrophilic
- Manganese Phosphate
- Nano-coating (Pallucid)
- Rolling Oil
- Rust Preventive Product
- Stearate Soap Lubricant/Dry-in-Place Lubricant (PULS)
- Trivalent Chromium/Non-Chromium
- Zinc Phosphate/Iron Phosphate
- Processing Services
- Laboratory Services
- Articles
- What's New
- Contact Us
- Privacy Policy
 |
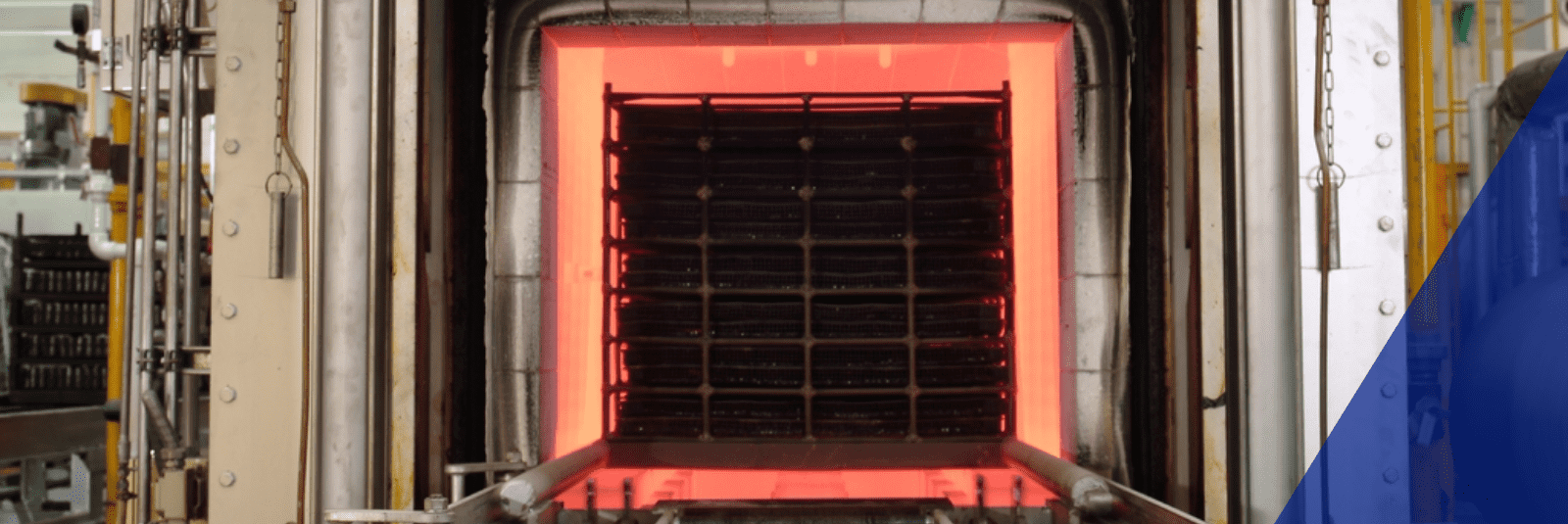
Gas Heat Treatment
Gas heat treatment is a heat treating process under various gas atmosphere and temperature mainly to improve hardness, wear resistance and fatigue or tensile strength properties of various mechanical steel parts. Thai Parkerizing can support various types of Gas heat treatment services as follow,
*Special process: Botan (Carbon protection process) Gas Carburizing Gas carburizing is a method to increase surface hardness of mild or low alloy steel by heating the steel to 850oC - 940oC. Sometimes it is necessary to prevent carburizing on certain areas of a part. Preventing carburization in selective areas can be done with mechanical masking or chemical coating (Botan process) Gas Carbonitriding The hardenability is improved by nitriding, it is possible to treat non-alloy steel such as SPCC and low carbon steel which cannot be applied by gas carburizing, and the reduction of material cost is also a great advantage. Since it can be quenched at a lower temperature than gas carburizing, deformation and distortion due to heat treatment can be reduced. Quenching and Tempering After that, tempering is usually performed for the purpose of providing toughness to the steel hardened by quenching. |
Get the info you’re looking for right now!
If you can’t find the answer you’re looking for, we’d love to hear from you – whether you’re curious about features, a sample trial, or even pricing—we’re ready to answer all questions a find the right products for you!
- Available to control surface hardness and case depth
- Available in 3 types of quenching oil (cold / semi hot / hot)
- Improve hardness, toughness and impact strength
- Improve wear resistance ability
- Improve fatigue strength
Mainly use with power units parts such as engines, transmissions, and differentials parts (connecting rod, crankshaft, transmission gear / shafts, CVT pulley shaft, drive shaft, constant velocity joint parts, final gear, differential side gear, etc.)
Product type
Check more of our Product / Process type specifications below.
Carbonitriding is a very interesting thermal process that offers several benefits for metal products. Here are the main benefits of carbonitriding heat treatment:
Benefits of Carbonitriding Heat Treatment
-
Increased Surface Hardness:
-
The process introduces both carbon and nitrogen simultaneously into the steel surface, forming nitrides and carbides, which are extremely hard and highly wear-resistant.
-
-
High Wear Resistance:
-
With the significant increase in surface hardness, carbonitrided parts have a longer service life and excellent resistance to abrasion and friction.
-
-
Core Toughness Retention:
-
While the surface is made hard and wear-resistant, the underlying metal (the core) retains its original toughness properties. This gives the part a good balance between surface hardness and impact resistance.
-
-
Retained Original Dimensions:
-
Carbonitriding alters the structure of the metal in the top surface layer; it does not create an additional layer on top of the steel (Hardened case is not an additional layer). Therefore, the original dimensions of the component are retained, which is highly beneficial for parts requiring high precision.
-
-
Lower Operating Temperature:
-
The carbonitriding process uses a lower temperature range (about 800ºC to 880ºC) compared to standard gas carburizing (about 850ºC to 940ºC). The lower temperature reduces the chance of part distortion.
-
-
Suitable for Non-alloy and Low Carbon Steel:
-
This process is particularly suitable for low carbon steel and non-alloy steel that would not achieve a hardened surface in standard gas carburizing.
-
In summary, carbonitriding is a better alternative for producing parts that require a hard surface with high wear resistance while maintaining core toughness and providing better distortion control, especially for low carbon steels.
Frequently Asked Questions
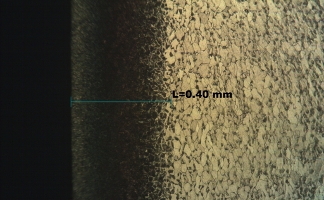
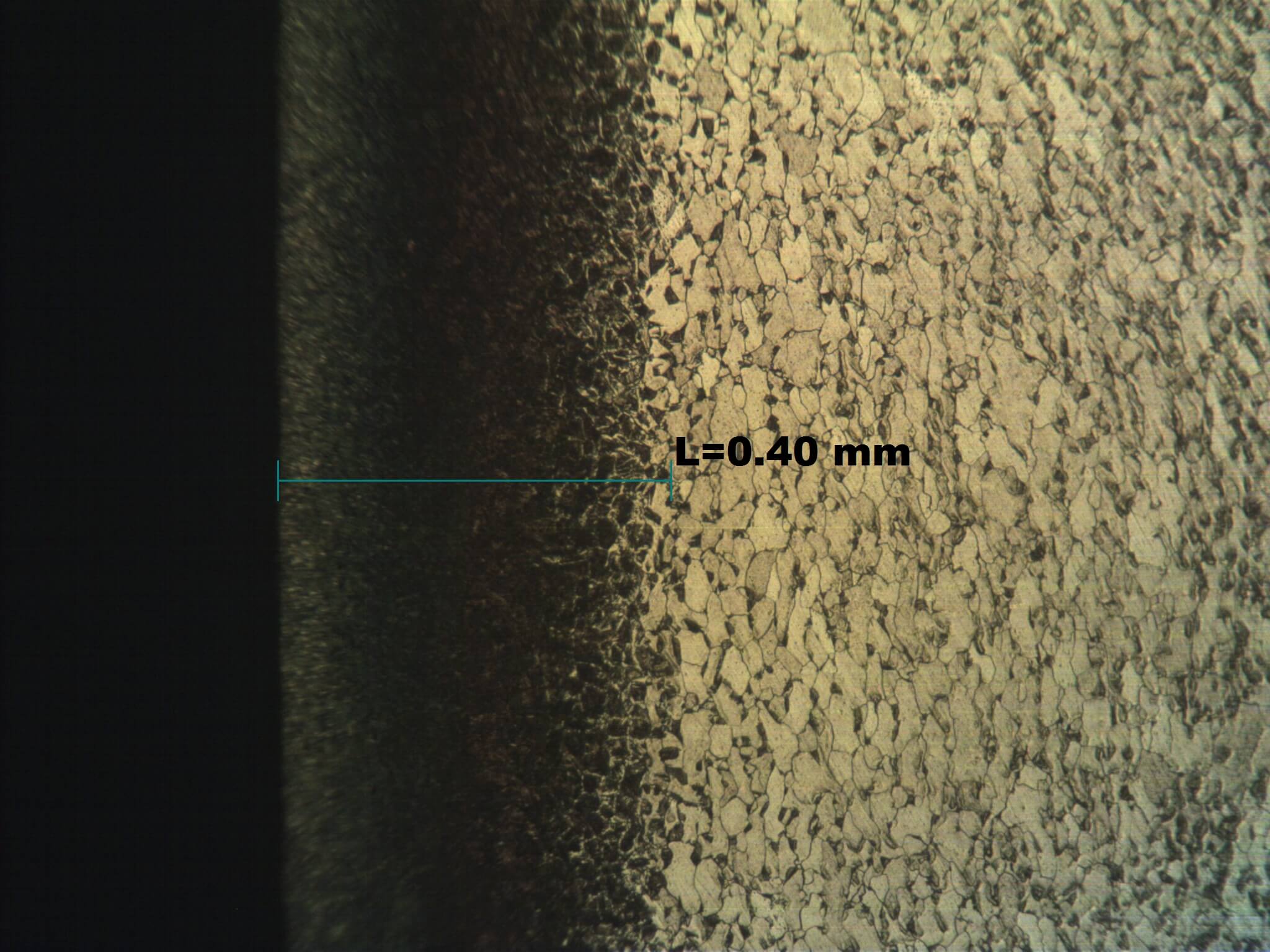
Carbonitriding is one of the heat-treating processes under various gas atmospheres and temperatures mainly to improve hardness, wear-resistance, and fatigue or tensile strength properties of industrial parts in order to prolong their lifespan and improve their properties to suit specific usability.
Carbonitriding is a process in which carbon and nitrogen are simultaneously infiltrated into the surface of steel at a temperature of about 800°C to 880°C, lower than ordinary gas carburizing, and then quenched and hardened. In gas carbonitriding, NH3 gas is added to a normal gas carburizing atmosphere, and nitriding and carburizing are performed simultaneously by
the N component decomposed from NH3. Since the hardenability is improved by nitriding, it is possible to treat non-alloy steel such as SPCC and low carbon steel which cannot be applied by gas carburizing, and the reduction of material cost is also a great advantage. Since it can be quenched at a lower temperature than gas carburizing, deformation, and distortion due to heat treatment can be reduced. Characteristics of gas carbonitriding are including
- Applicable steel type: Low carbon steel (low carbon steel such as SP material, SS material, S10C), case hardening steel (low carbon alloy steel such as SCM, SCr, SNCM)
- Quenching is possible at low temperatures, reducing quench deformation (Excluding case-hardened steel)
- Since the hardenability is improved by the influence of nitrogen, quenching becomes easy even with carbon steel, which is advantageous in terms of quenching cracking.
- Compared to gas carburization, the abnormal hardening layer on the outermost surface is suppressed, and a uniform hardened layer can be generated.
- Improved temper softening resistance compared to gas carburizing.
This process is important because it can improve the mechanical properties of the metal, such as its hardness and toughness. In addition, carbonitriding can also help to protect the metal from corrosion.
The carbonitriding process usually applies with power units parts such as engines, transmissions, and differentials parts (connecting rod, crankshaft, transmission gear/shafts, CVT pulley shaft, driveshaft, constant velocity joint parts, final gear, differential side gear, etc.)